Exercice 1: Benchmarking a simple application locally
1. Pre-requisites
For this exercise, we will use GitHub codespaces to benchmark a simple application using feelpp.benchmarking.
1.1. GitHub Codespaces
-
First, log in to your GitHub account and navigate to your assignment repository.
-
On the top-left branches button, select the feedback branch. (This is because we do not want the Docker configuration from the CI/CD course to interfere with this exercice).
-
Click again on that button, and write benchmarking. Now click on create branch benchmarking from the feedback branch.
-
In this branch, go to the Code button and create a new codespace for the benchmarking branch.
-
Inside the codespace, DELETE the .devcontainer folder to use the default image. If you want, you can actually delete everything in the repository and start from scratch.
-
Rebuild the codespace.
1.2. Install feelpp.benchmarking
feelpp.benchmarking is available on PyPI and can be installed using pip:
pip install feelpp-benchmarking1.3. Create a .gitignore file
The next steps will create a large number of files and directories that are not necessary to be tracked by Git. To avoid cluttering the repository, create a .gitignore file in the root of your project, or update the existing one.
touch .gitignoreAnd add the following content:
node_modules/
package-lock.json
public/
cache/
reframe/
reports/
outputs/1.4. Initialize antora environment
In order to generate the benchmark reports website, the Antora environment must be configured beforehand.
Initialize the Antora environment in the current directory. There is a built-in script that automates this process:
feelpp-antora init -d . -t "My Benchmarks" -n my_benchmarks1.5. Verify the setup
You should see the following files and directories created on the root of your project:
-
site.yml: The antora playbook file. -
docs/: The directory where the dashboard Asciidoc pages are stored. -
package.json: The nodejs package file, containing necessary dependencies for feelpp.benchmarking. -
package-lock.json: The lock file for the nodejs package. -
node_modules/: The directory where the nodejs dependencies are stored.
To see if our dashboard is correctly configured, compile the Asciidoc files to HTML and start a web server:
npm run antora
npm run startFinally, click on the link on the terminal to open the dashboard in your browser.
If everything OK, you should see a page with the title My Benchmarks.
Close the server by pressing Ctrl+C on the terminal.
2. Copy the system configuration file
To benchmark applications on a machine, a ReFrame configuration file must be provided to feelpp.benchmarking. This file describes the system’s architecture, as well as the necessary modules, partitions, commands, and environments for your applications to run as expected.
Create a new Python file named codespace_machine.py in the root of your project
touch codespace_machine.pyand copy the following content to the file:
site_configuration = {
'systems': [
{
'name': 'codespace_machine',
'descr': 'GitHub Codespace Machine',
'hostnames':['py::socket.gethostname'],
'partitions': [
{
'name': 'my_partition',
'scheduler': 'local',
'launcher': 'local',
'environs': ['my_environment'],
'processor': { 'num_cpus': 1 }
}
]
}
],
'environments':[
{
'name': 'my_environment',
'target_systems': ["codespace_machine:my_partition"]
}
]
}3. Create a Machine Specification File
Create a new JSON file names codespace_specs.json in the root of your project
touch codespace_specs.jsonand copy the following template:
{
"machine": "<TODO>",
"targets":["<TODO>:builtin:<TODO>"],
"reframe_base_dir":"<TODO>",
"reports_base_dir":"<TODO>",
//HELP: The input_dataset_base_dir can be used to indicate where benchmarked application can be found.
"input_dataset_base_dir":"<TODO>",
"output_app_dir":"<TODO>"
}
|
Solution
{
"machine": "codespace_machine",
"targets":["my_partition:builtin:my_environment"],
"reframe_base_dir":"$PWD/reframe",
"reports_base_dir":"$PWD/reports",
"input_dataset_base_dir":"$PWD/examples",
"output_app_dir":"$PWD/outputs"
}4. Example application
For this exercise, we will use a simple Python application that calculates the n’th Fibonacci number, in two different ways: recursively and iteratively.
It takes the following arguments:
-
-n: the sequence number to calculate -
-a: the approach to use. Options arerecursiveanditerative -
-o: the output file to write the elapsed time. It will be saved in CSV format (elapsed,fibonacci_number)
Create a new folder named examples/ and a Python file named fibonacci.py inside the examples folder.
mkdir examples
touch examples/fibonacci.pyand copy the following content to the file:
from argparse import ArgumentParser
import os
from time import perf_counter
def fibonacciRecursive(n):
if n < 1: return 0
elif n <= 2: return 1
else: return fibonacciRecursive(n-1) + fibonacciRecursive(n-2)
def fibonacciIterative(n):
if n < 1: return 0
elif n <= 2: return 1
else:
a,b = 1,1
for i in range(3,n+1):
a,b = b,a+b
return b
if __name__=="__main__":
parser = ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('-n',type=int,help="Sequence number",required=True)
parser.add_argument('--approach','-a',type=str, help="Fibonacci algorithm approach to use",required=True)
parser.add_argument('--out','-o',type=str, help="Filepath where to save elapsed times",required=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
n = int(args.n)
if args.approach == "recursive":
fib = fibonacciRecursive
elif args.approach == "iterative":
fib = fibonacciIterative
else:
raise NotImplementedError(f"Fibonacci approach - {args.approach} - not implemented")
tic = perf_counter()
fib_number = fib(n)
toc = perf_counter()
elapsed_time = toc - tic
dirpath = os.path.dirname(args.out)
if not os.path.exists(dirpath):
os.makedirs(dirpath)
with open(args.out,'w') as f:
f.write(f"elapsed,fibonacci_number\n{elapsed_time},{fib_number}")
print(f"Elapsed time: {elapsed_time}")
print(f"Fibonacci number: {fib_number}")
print("Done!")5. Create a Benchmark Specification File
Once how the application that will benchmarked works is understood, a benchmark specification file must be created to describe how the application will be tested.
Create a new JSON file named fibonacci_benchmark.json in the root of your project
touch fibonacci_benchmark.jsonand copy the following template:
{
"use_case_name":"Fibonacci",
"timeout":"0-0:5:0",
"executable": "python <TODO>/fibonacci.py",
"output_dir":"<TODO>",
"options":[
"-n <TODO>",
"-a <TODO>",
"-o <TODO>/output.json"
],
"scalability": {
"directory":"<TODO>",
"stages":[
{
"name":"",
"filepath":"output.json",
"format":"csv",
"units":{ "fibonacci_number":"" }
}
]
},
"sanity":{ "success":["<TODO>"] },
"resources": {"tasks":1, "exclusive_access":false },
"parameters": [
{
"name":"n",
//Equivalent to: "sequence":[10,15,20,25,30,35,40]
"range":{"min":10,"max":40,"step":5}
},
{
"name":"method",
"sequence":["recursive","iterative"]
}
]
}
|
Solution
{
"use_case_name":"Fibonacci",
"timeout":"0-0:5:0",
"executable": "python {{machine.input_dataset_base_dir}}/fibonacci.py",
"output_dir":"{{machine.output_app_dir}}/fibo",
"options":[
"-n {{parameters.n.value}}",
"-a {{parameters.method.value}}",
"-o {{output_dir}}/output.json"
],
"scalability": {
"directory":"{{output_dir}}",
"stages":[
{
"name":"",
"filepath":"output.json",
"format":"csv",
"units":{ "fibonacci_number":"" }
}
]
},
"sanity":{ "success":["Done!"] },
"resources": {"tasks":1, "exclusive_access":false },
"parameters": [
{
"name":"n",
"range":{"min":10,"max":40,"step":5}
},
{
"name":"method",
"sequence":["recursive","iterative"]
}
]
}6. Create a Figure Description File
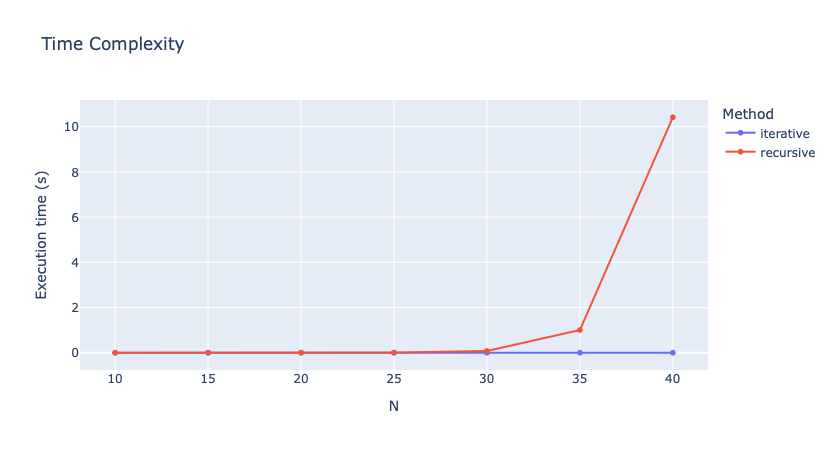
To immediately be able to visualize the results of the benchmark, a figure description file must be created.
Create a new JSON file named fibonacci_plot.json in the root of your project
touch fibonacci_plot.jsonand copy the following template:
{
"plots":[
{
"title":"Time Complexity",
"plot_types":["scatter"],
"transformation":"performance",
"variables": ["elapsed"],
"xaxis":{ "parameter":"<TODO>", "label":"<TODO>" },
"yaxis": {"label":"Execution time (s)"},
"color_axis":{"parameter":"<TODO>","label":"<TODO>"}
}
]
}Solution
{
"plots":[
{
"title":"Time Complexity",
"plot_types":["scatter"],
"transformation":"performance",
"variables": ["elapsed"],
"xaxis":{ "parameter":"n", "label":"N" },
"yaxis": {"label":"Execution time (s)"},
"color_axis":{"parameter":"method","label":"Method"}
}
]
}7. Run the benchmark and visualize the results
To launch the benchmarks, use the following command:
feelpp-benchmarking-exec --machine-config codespace_specs.json \
--custom-rfm-config codespace_machine.py \
--benchmark-config fibonacci_benchmark.json \
--plots-config fibonacci_plot.json \
--website
The --website flag will generate the dashboard files and start a web server to visualize the results.
|
 .pdf
.pdf