Continuous benchmarking
It is possible to configure a workflow for feelpp.benchmarking to continuously benchmark an application. This will allow users to:
-
Centralize benchmark results in a dashboard
-
Connect the CB pipeline to an existing CI pipeline
-
Ensure non-regression and analyse the performance over time
-
Compare the performance of different versions of the application
1. Launching a benchmark
Currently, the workflow is not directly available from feelpp.benchmarking. However, a template repository is coming soon to help users set up the workflow.
In order to have this workflow running, self-hosted runners for your machines are required. And one "default" runner is needed to orchestrate launching the application on different machines.
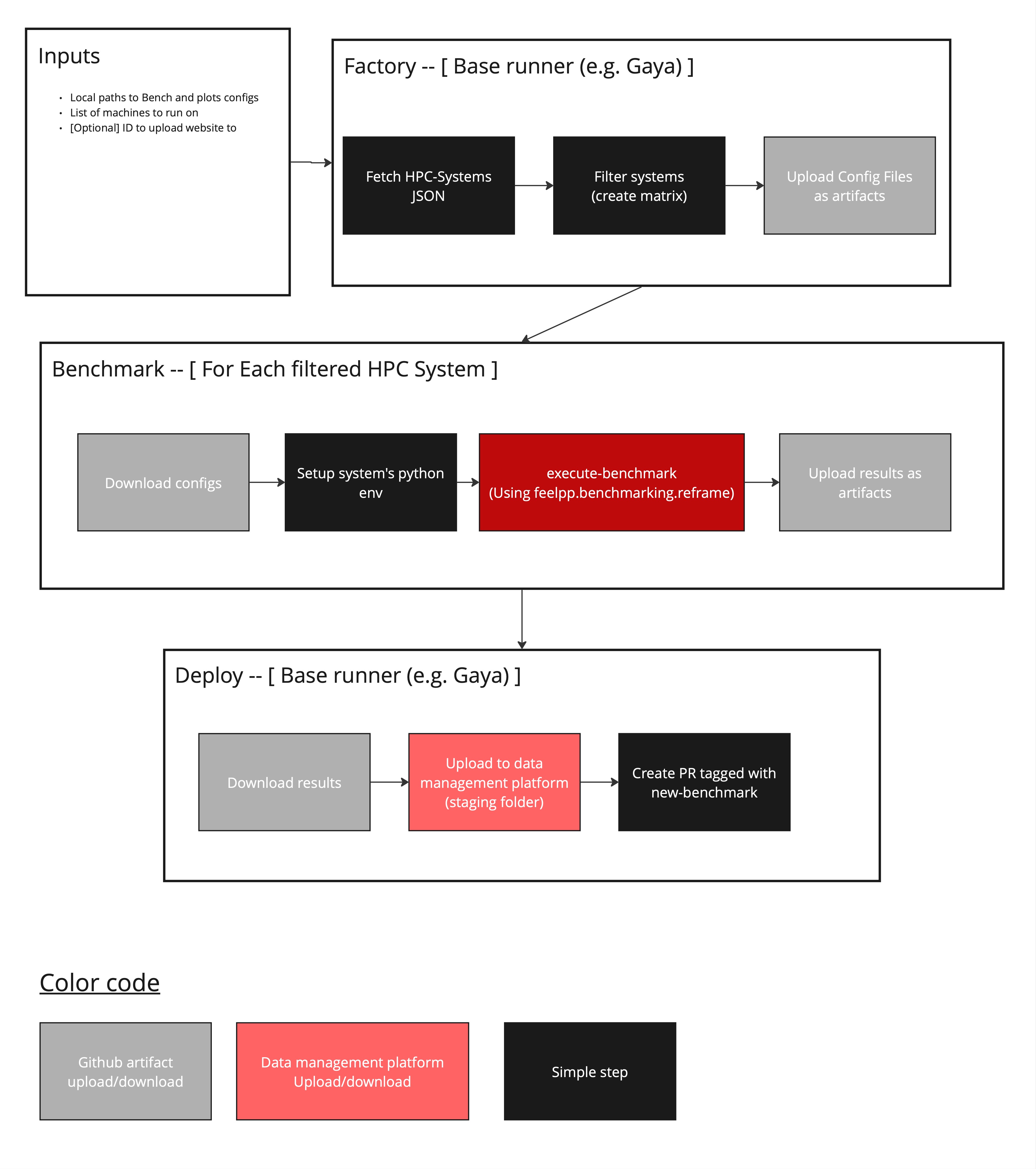
-
The workflow takes as input: the benchmark configurations paths, a list of machines to run, and optionally a Girder ID to updload the website to (more data management platorms will be supported in the future).
-
In a default runner (can even be a GitHub hosted runner), machine specification files are read and filtered by the given machine name list input. This allows to launch the application on multiple machines. Then, a "Matrix" is created to later tell the workflow what runners to launch.
-
Then, only desired machine configurations are uploaded as GitHub artifacts.
-
On each HPC system, the machine configuration is downloaded.
-
A Python environment is then set up, depending on the system. (e.g. loading necessary modules, creating the python virtual environment, downloading
feelpp-benchmarking). -
feelpp.benchmarking launches all parametrized tests using the
feelpp-benchmarking-execcommand. -
When benchmarks are done, results are uploaded as GitHub artifacts in order to communicate them with the default runner.
-
The default runner then collects all results and uploads them to the data management platform.
-
If a custom remote ID is provided to upload the dashboard to, the dashboard is uploaded to the data management platform. Otherwise, a pull request tagged with
new-benchmarkis created to preview the results. We do the preview with Netlify.
|
This workflow requires setting up the Girder data management platform so that it contains to following folders: |
2. Deploying the dashboard
GitHub pages can be configured to have a persistent dashboard containing benchmarks. But we want to have only pertinent benchmarks on this publicly available dashboard. To do so, the following workflow is proposed.
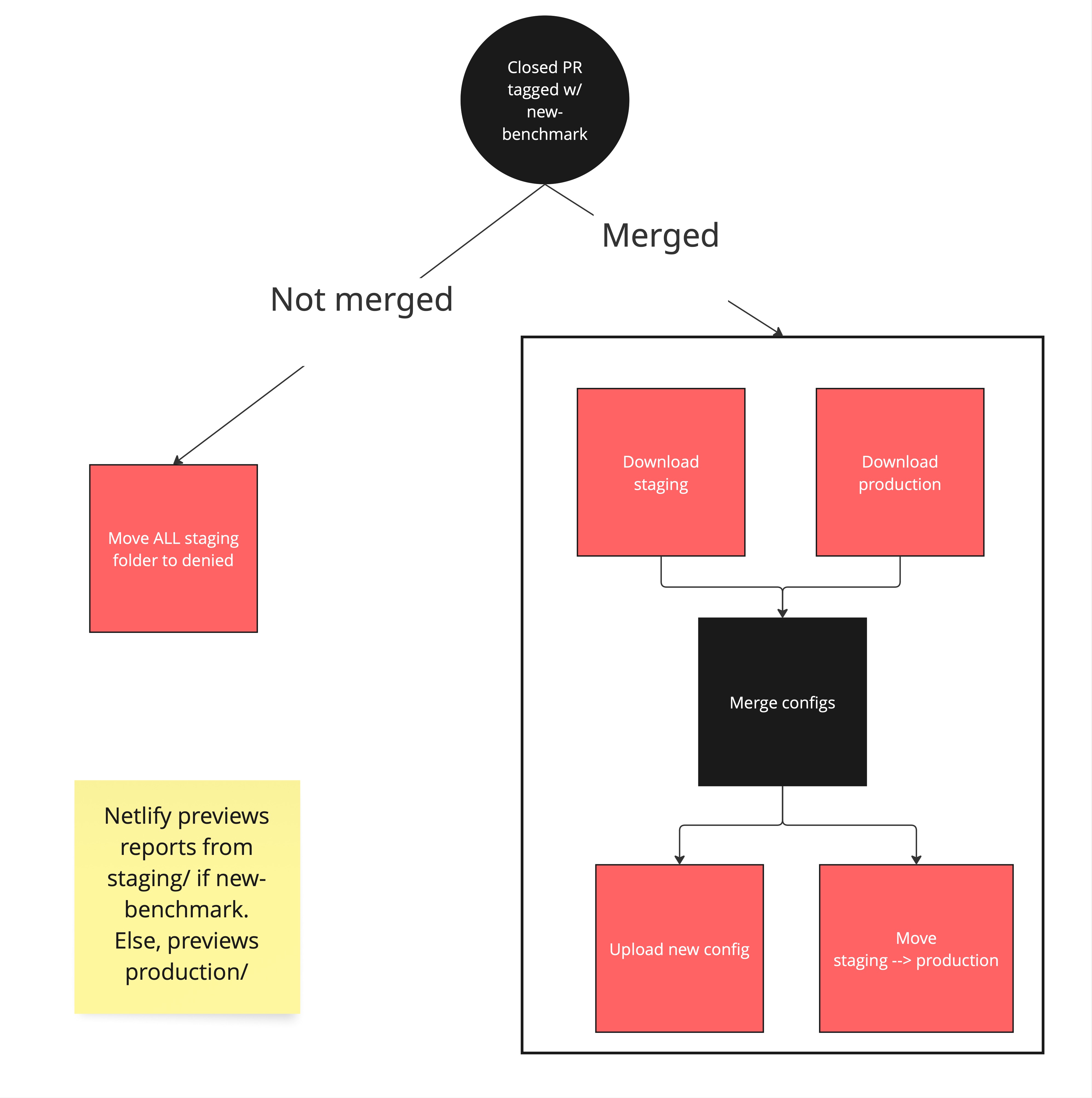
-
When a pull request tagged with
new-benchmarkis closed, the deploy.yml workflow is launched. -
If the pull request is closed, all benchmarks present on the
staging/folder are moved to thedeniedfolder (on the data management platform). -
If the pull request is merged, staging and production dashboard configuration files are downloaded.
-
Both configuration files are merged, so that staging benchmarks are added to the production dashboard.
-
The new dashboard configuration is uploaded, and staging benchmarks are moved to production.
-
This will trigger the GitHub pages deployment, having all production benchmarks.
 .pdf
.pdf